The Reference
The first step of RNA-seq data analysis is to choose your reference, either a genome or transcriptome.
Aligning against a genome
- Data is visualized in the context of the whole genome.
- Allows to discover new transcripts.
Aligning against a transcriptome
- Quantification can be more accurate
- Needs less resources
Which one should I use?
If possible use both, as each of them may reveal a different aspect of your system.
Only by seeing the data in the context of genome and transcriptome will you fully appreciate the complexity of the task at hand
Alignment-based quantification
- Can be applied for both a transcriptome or genome reference.
- This method involves mapping the RNA-seq reads to the reference.
If working with a genome reference a splice-aware
software is required such as: hisat2 or
minimap2.
Feature Quantification
Once you have the alignment files (SAM/BAM files), the next step is to assign a specific value to a genomic feature. This method requires an annotation file that lists the intervals of these features (GFF file).
“Feature counting” involves counting how many reads overlaps the intervals listed in the annotation file.
What constitutes overlap?
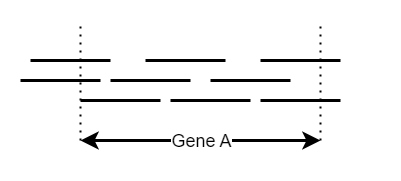
- How many reads complete overlap gene A?
- How many reads overlap gene A at all?
As always there is no correct method for defining overlap, and the researcher must choose the one that is more appropriate for each case.
Most commonly used tool for feature quantification of BAM files is
featureCounts and htseq-count. However, the
way that you count also has some ambiguity.
Classification-based quantification
- Can only be used with as transcriptome as reference
- Produces “pseudo-alignments”
- When reads can be assigned to various transcripts, the software uses a redistribution algorithm.
Classification-based methods combine “alignment” and quantification in the same step which may increase accuracy at detecting transcript abundances. However, the redistribution algorithm works as a black box may make difficult to understand why a particular transcript was differentially expressed.
Since each assembled transcript is used as the feature to count, it does not necessarily need an annotation file.
The two more used tools for classification of RNA-seq reads are
kallisto and salmon.